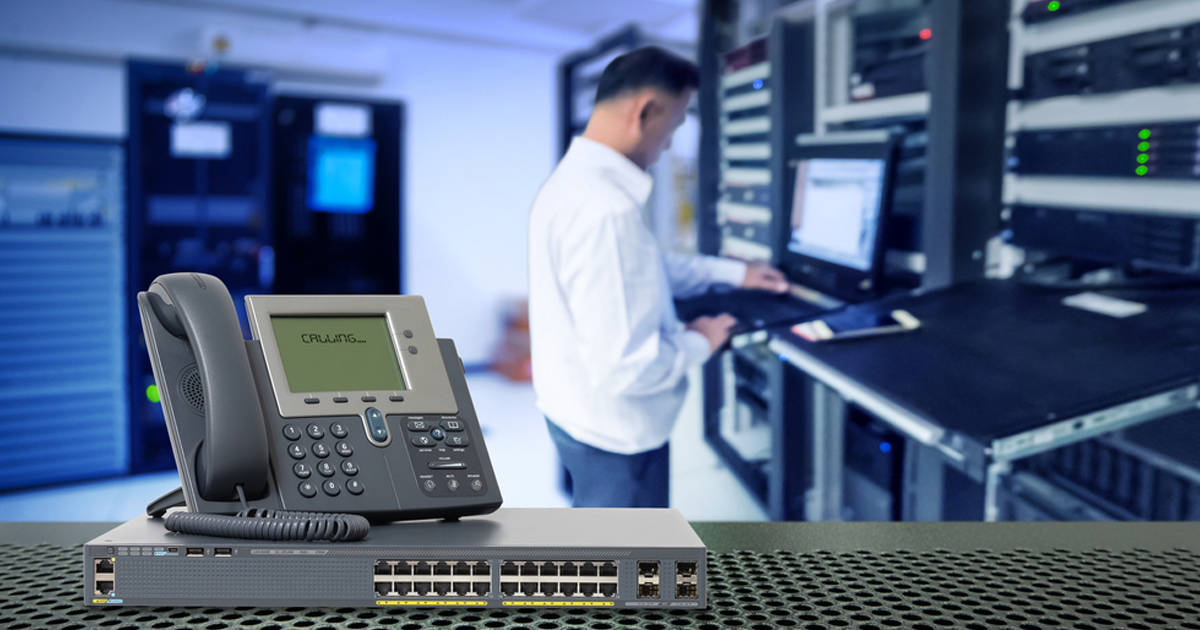
Responsible for transmitting audio and video data in real time, RTP, or Real-time Transport Protocol, is a protocol used in voice over IP (VoIP) communications. Generally used in conjunction with SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), provides quality of service control during its communications to ensure the delivery of data packets in real time with the lowest possible latency.
Its versatility allows the configuration of several media options with different sampling rates, that is, it is compatible with several codecs audio and video. Due to this versatility, there are different types of applications and devices capable of successfully communicating using the protocol.
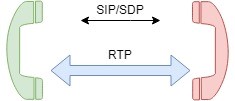
On the net RCTS VoIP, during a call, after signaling (SIP – Session Initiation Protocol) RTP comes into play. RTP creates multiple audio samples and, using a numbering system, inserts them into multiple datagrams to ensure that the packets are delivered in the correct order. These packets contain timestamps to control the data playback time and adjust the playback speed. Since this is a real-time protocol, transport speed is a priority, so RTP will use the Datagram Protocol (UDP) to send data.
A good analogy to understand RTP is to imagine a mail system:
- 1st Due to the complexity and size of the message, RTP takes several samples of the message and encapsulates the data into several small letters (packets) with a destination address and a sequence number.
- 2nd Then the letters are sent, separately, to the delivery process where they may face congestion, delays, deviations and losses.
- 3rd Upon reception, the RTP receiver analyzes each letter to check for errors and guides them, using their sequential number, to the correct order for each letter, putting the small parts together like a puzzle and delivering the complete message to the application.
What is RTCP?
THE RTCP It's similar to RTP, but it doesn't transport media data, but rather controls that data. Through feedback on this data, RTCP generates reports on transmission quality, including packet loss and delay rates, helping to synchronize time between the source and destination. For a good real-time communication experience, both protocols are necessary.
In short, RTP is the most widely used real-time transport protocol for voice and video transmissions and is specifically used in the RCTS VoIP network. It is through this protocol that, after signaling (SIP – Session Initiation Protocol) occur in calls, it is possible to hear the voice of the person we are calling and vice versa.